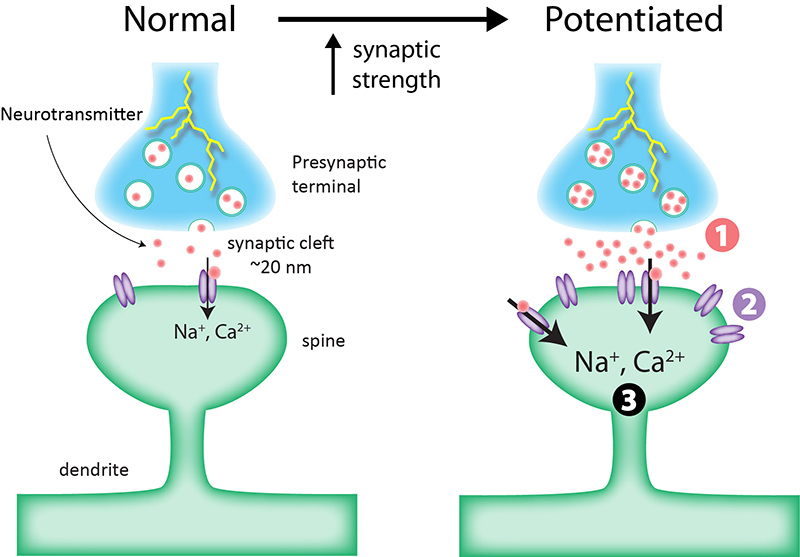
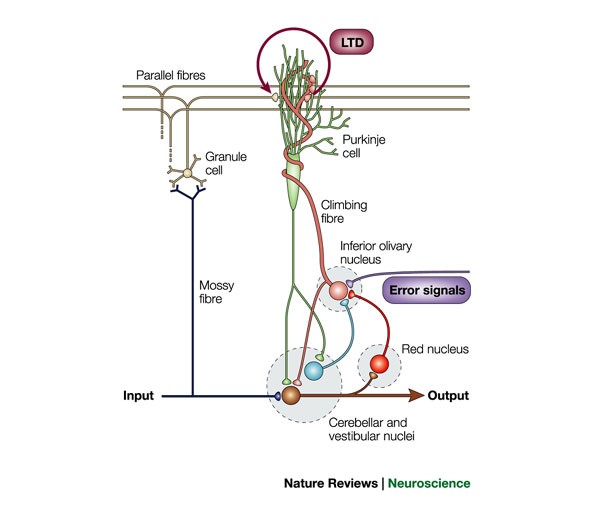
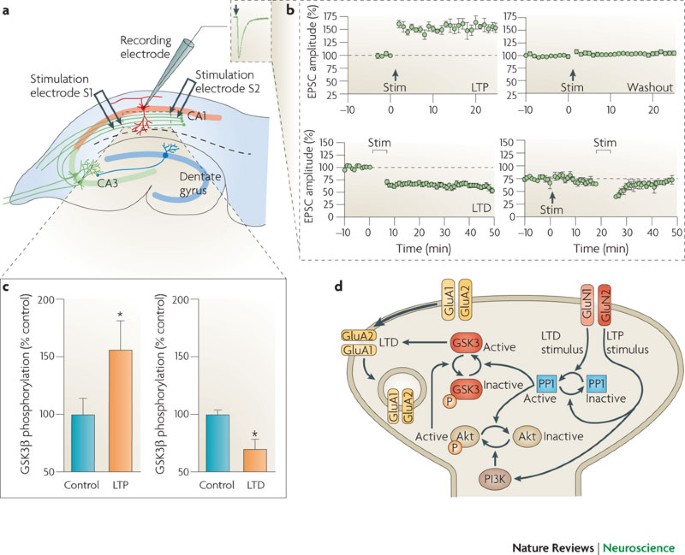
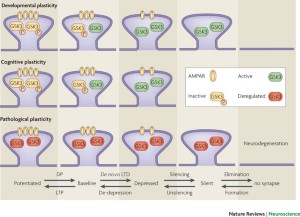
Hippocampal long-term depression mediates acute stress-induced spatial memory retrieval impairment | PNAS

What is the Difference Between Long-term Depression and Long-term Potentiation | Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms

Model of regulated AMPAR endocytosis during long-term depression intwo... | Download Scientific Diagram

A Molecular Switch for Induction of Long-Term Depression of Corticostriatal Transmission | Journal of Neuroscience
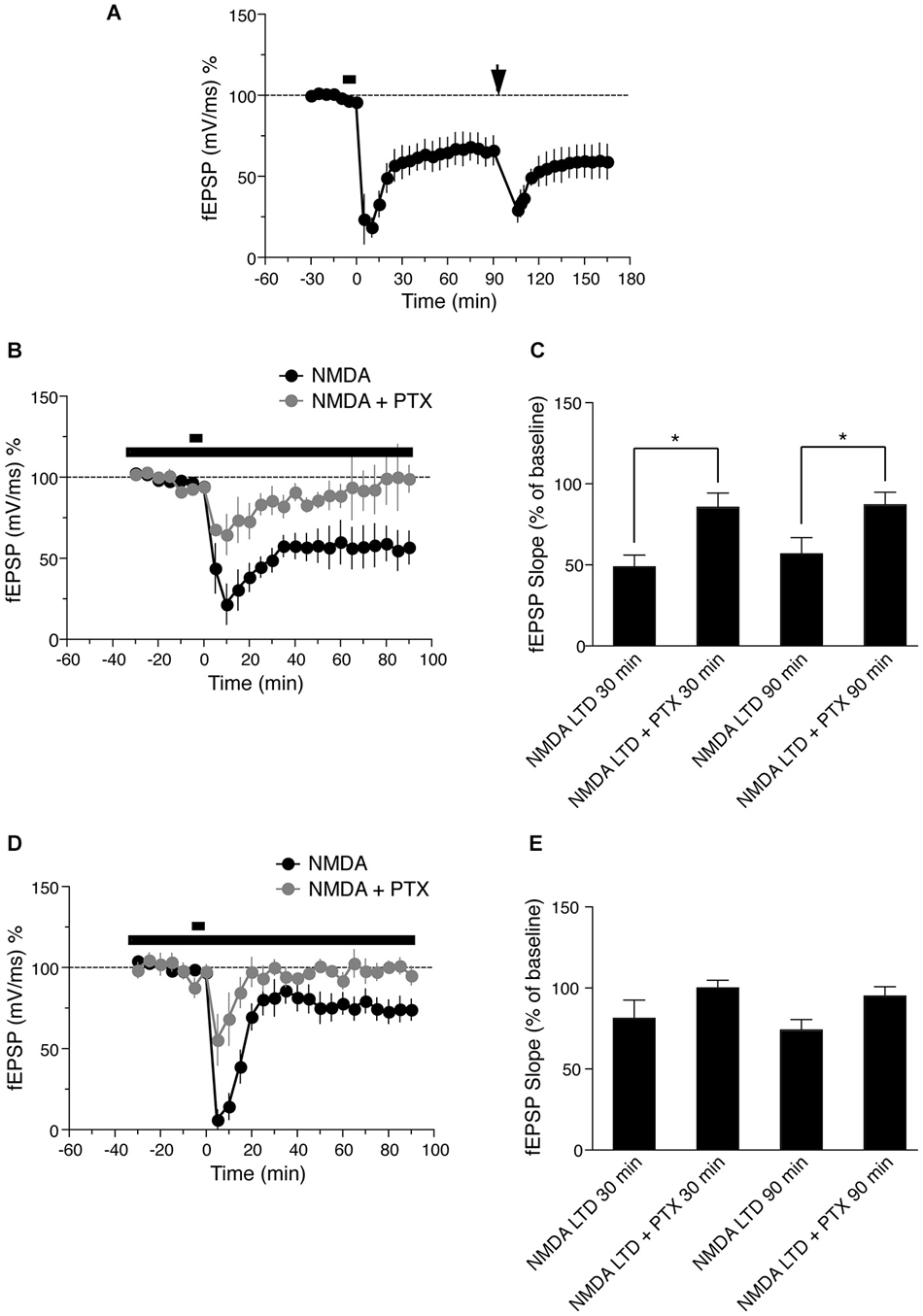
Frontiers | Long-term depression is differentially expressed in distinct lamina of hippocampal CA1 dendrites

Long-term depression: a cell biological view | Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences

Revisiting the flip side: Long-term depression of synaptic efficacy in the hippocampus | Semantic Scholar